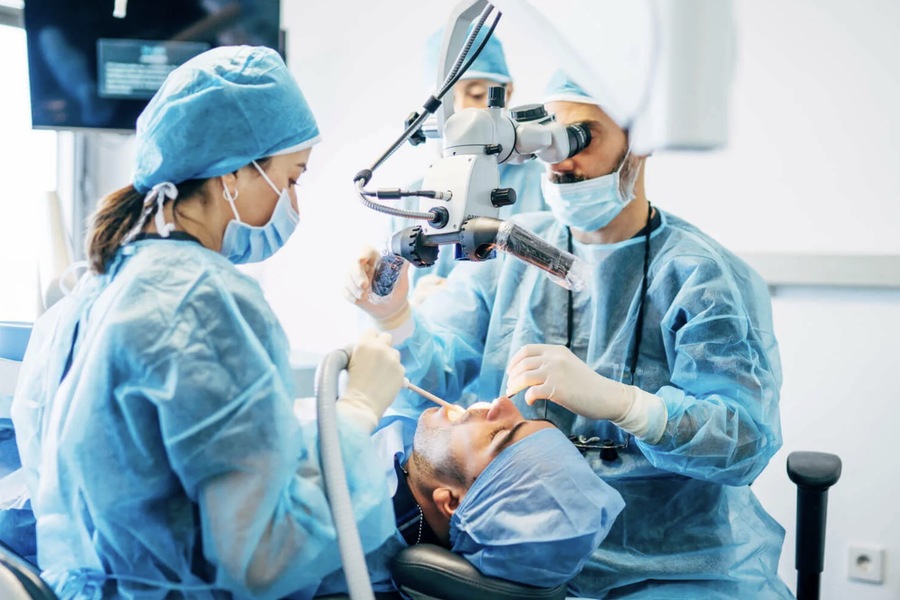
Pain management is critical to oral surgery, impacting patient comfort, recovery, and overall experience in a dental clinic. Over the years, significant advancements have been made in this area, leading to more effective and personalized pain management strategies. This article traces the evolution of pain management in oral surgery, highlighting key milestones and the latest techniques that are reshaping patient care.
Early Approaches to Pain Management
In the early days of oral surgery, pain management options were limited, often relying on basic analgesics and rudimentary anesthesia techniques. While somewhat effective, these methods lacked precision and usually led to significant discomfort during and after procedures.
Traditional Analgesics: Common analgesics, such as aspirin and acetaminophen, were the primary means of managing pain. However, these drugs were not always sufficient, especially for more invasive procedures.
General Anesthesia: In more complex surgeries, general anesthesia was often used to ensure the patient remained unconscious throughout the procedure. While effective, this approach carried risks and required careful monitoring.
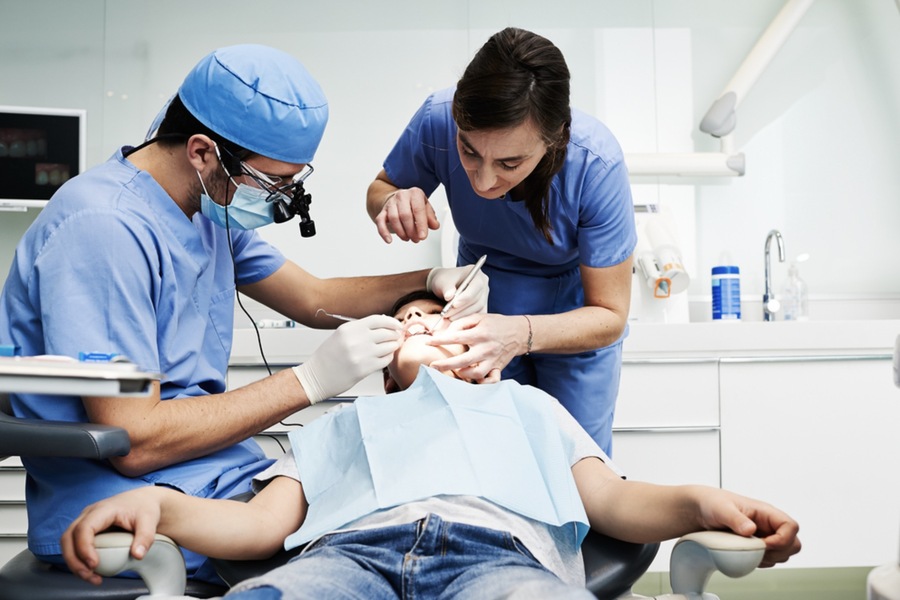
Modern Advancements in Pain Management
The evolution of pain management in oral surgery has been marked by the development of more advanced techniques and medications to improve patient comfort and safety.
Local Anesthesia: Introducing local anesthetics, such as lidocaine, revolutionized pain management in oral surgery. These drugs allow for targeted pain relief, numbing only the specific area being treated. According to a study in the Journal of Dental Research (2021), local anesthesia has reduced patient discomfort during oral surgery by 70%.
Sedation Techniques: Modern sedation techniques, including intravenous (IV) sedation and oral sedatives, have made it possible to manage anxiety and pain more effectively. These methods balance consciousness and pain relief, allowing patients to remain calm and comfortable during procedures.
Multimodal Pain Management: Multimodal pain management strategies, which combine different types of analgesics and anesthetics, have been shown to enhance pain control and reduce the need for opioids. A study in the Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (2020) found that multimodal approaches can reduce postoperative pain by 40% and decrease opioid consumption by 50%.
The Role of Technology in Pain Management
Advancements in technology have also played a significant role in the evolution of pain management in oral surgery.
Laser Dentistry: Laser technology has minimized pain during gum surgery and cavity treatment procedures. Lasers reduce the need for incisions and stitches, leading to faster healing and less postoperative discomfort.
3D Imaging and Guided Surgery: These technologies allow for more precise surgical planning, reducing the trauma to surrounding tissues and nerves. This precision translates to less postoperative pain and quicker recovery times.
The Future of Pain Management in Oral Surgery
Continued advancements in pharmacology and technology will likely shape the future of pain management in oral surgery. Emerging techniques, such as the use of nerve regeneration inhibitors and non-opioid pain medications, promise to reduce pain further and enhance patient outcomes.
Conclusion
The evolution of pain management in oral surgery has significantly improved the patient experience, making procedures safer and more comfortable than ever before. By embracing modern techniques and technologies, oral surgeons can provide effective pain relief tailored to each patient’s needs. As the field continues to advance, patients can expect even greater improvements in pain management, leading to faster recoveries and better overall outcomes.
Skydiver, feminist, band member, Mad Men fan and holistic designer. Acting at the crossroads of modernism and intellectual purity to craft delightful brand experiences. Let’s design a world that’s thoughtful, considered and aesthetically pleasing.